AI tutor
Full solution
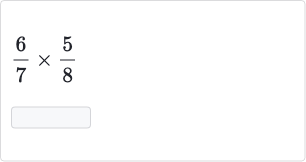
Q.
- Multiply Numerators and Denominators: To find the product, multiply the numerators together and the denominators together.
- Multiply Numerators: Now, multiply the numerators: .
- Multiply Denominators: Next, multiply the denominators: .
- Find Product: So, the product is . But wait, we can simplify this fraction.
- Simplify Fraction: Both and are divisible by . and \).\ So, simplifies to .