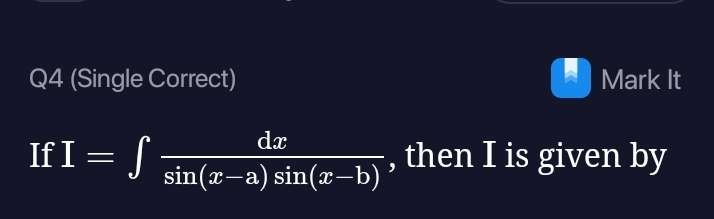AI tutor
Full solution
Q. If , then is given by
- Apply Trigonometric Identity: Let's use the identity to simplify the integral.So, .
- Simplify the Integral: This simplifies to . Now,
- Factor Out Constants: We can take out the constant term and from the denominator, so .
- Use Substitution: Now, let's use the substitution , which means . So, .
- Integrate with Substitution: Substitute back into the integral, we get . This simplifies to .
- Split Integral: Now, we can split the integral into two parts: .
- Evaluate First Integral: The first integral is just since is a constant.
- Evaluate Second Integral: The second integral is a standard integral that equals .
- Combine Results: So, , where is the constant of integration.
- Substitute Back and Simplify: Now, substitute back to get in terms of .
.