AI tutor
Full solution
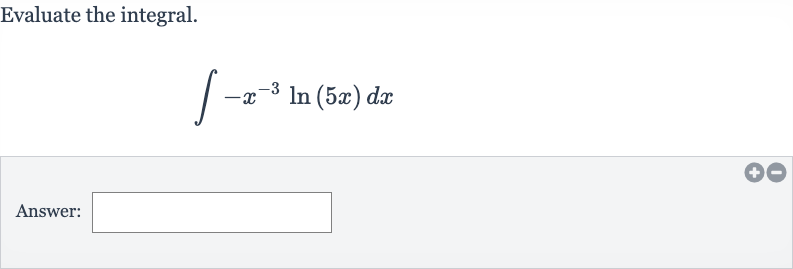
Q. Evaluate the integral.Answer:
- Recognize Integral Type: Recognize that the integral involves a logarithmic function multiplied by a power of . This suggests that integration by parts may be a useful technique. The integration by parts formula is .
- Choose and : Choose and for the integration by parts. Let and . Then we need to compute and . Differentiating gives , and integrating gives .
- Compute du and v: Compute du and v. We have and .
- Apply Integration by Parts: Apply the integration by parts formula. We have .
- Simplify Integral: Simplify the integral . This simplifies to .
- Integrate Simplified Integral: Integrate . The integral of with respect to is .
- Combine Integration Results: Combine the results from integration by parts. We have
- Add Constant of Integration: Add the constant of integration to the result. The final answer is .