AI tutor
Full solution
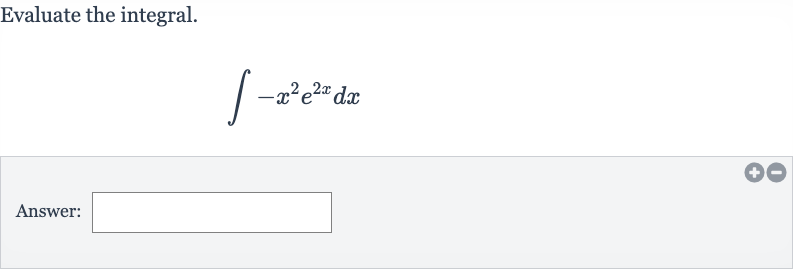
Q. Evaluate the integral.Answer:
- Integration by Parts: We will use integration by parts to evaluate the integral of with respect to . Integration by parts is given by the formula , where and are parts of the integrand that we choose. We will let (which means ) and (which means ). Now we will calculate and .
- Calculate and : First, we calculate by differentiating . The derivative of with respect to is , so .
- Apply Integration by Parts: Next, we find by integrating . The integral of with respect to is , so .
- Simplify the Expression: Now we apply the integration by parts formula: . Substituting the values of , , and , we get:.
- Integrate by Parts Again: Simplify the expression: .
- Calculate and : We need to integrate again by parts. Let (which means ) and (which means ). We calculate and again.
- Apply Integration by Parts Again: Calculate by differentiating . The derivative of with respect to is , so .
- Simplify the Expression: Find by integrating again. As before, the integral of with respect to is , so .
- Integrate : Apply the integration by parts formula again: . Substituting the new values of , , and , we get: .
- Combine All Parts: Simplify the expression:
- Final Answer: Now we integrate . The integral of with respect to is , so we get:.
- Final Answer: Now we integrate . The integral of with respect to is , so we get:.Combine all the parts together to get the final answer:, where is the constant of integration.
- Final Answer: Now we integrate . The integral of with respect to is , so we get:.Combine all the parts together to get the final answer:, where is the constant of integration.Simplify the expression to get the final answer:.