Full solution
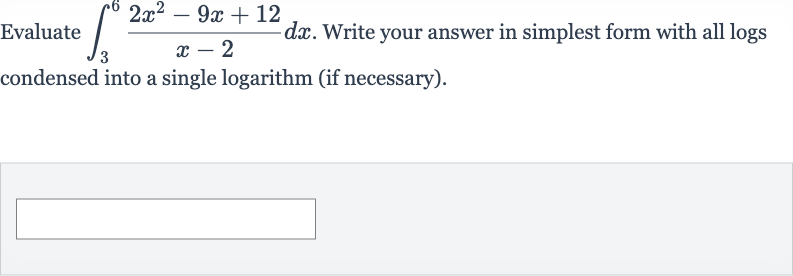
Q. Evaluate . Write your answer in simplest form with all logs condensed into a single logarithm (if necessary).
- Perform Polynomial Division: First, we need to perform polynomial long division or synthetic division to simplify the integrand since the numerator is a polynomial of higher degree than the denominator.
- Integrate Simplified Function: Performing the polynomial long division, we divide by : ___________x - | - () ___________ - () ___________ The result of the division is with a remainder of . So, the integrand can be rewritten as:
- Evaluate Definite Integral: Now we can integrate the function term by term:
- Substitute Values: Integrating each term gives us:So the indefinite integral is:
- Simplify Final Answer: Now we need to evaluate the definite integral from to . We do this by substituting the upper and lower limits into the indefinite integral and finding the difference:
- Simplify Final Answer: Now we need to evaluate the definite integral from to . We do this by substituting the upper and lower limits into the indefinite integral and finding the difference: Substitute the values and simplify: = = =
- Simplify Final Answer: Now we need to evaluate the definite integral from to . We do this by substituting the upper and lower limits into the indefinite integral and finding the difference: Substitute the values and simplify: = = = Since is , we can simplify further:
- Simplify Final Answer: Now we need to evaluate the definite integral from to . We do this by substituting the upper and lower limits into the indefinite integral and finding the difference: Substitute the values and simplify: = = = Since is , we can simplify further: The final answer in simplest form with all logs condensed into a single logarithm is: