Full solution
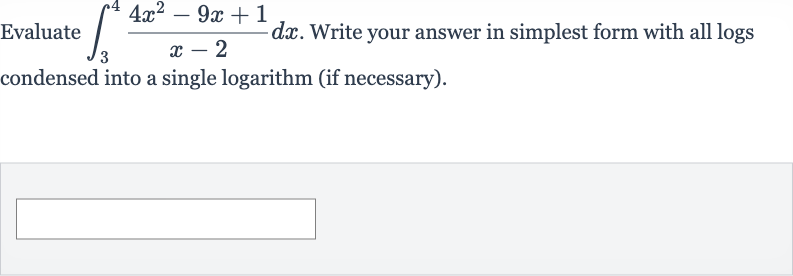
Q. Evaluate . Write your answer in simplest form with all logs condensed into a single logarithm (if necessary).
- Perform Polynomial Long Division: We will first perform polynomial long division to simplify the integrand .
- Simplify Integrand: Performing the division, we get: with a remainder of .So, .
- Write Integral as Sum: Now we can write the integral as the sum of two simpler integrals:.
- Integrate Each Term: We will integrate each term separately:and.
- Evaluate Definite Integral: Now we evaluate the definite integral from to :.
- Upper Limit Calculation: Plugging in the upper limit :.
- Lower Limit Calculation: Plugging in the lower limit :.
- Subtract Values: Subtract the value at the lower limit from the value at the upper limit:.
- Final Answer: The final answer in simplest form with all logs condensed into a single logarithm is:.