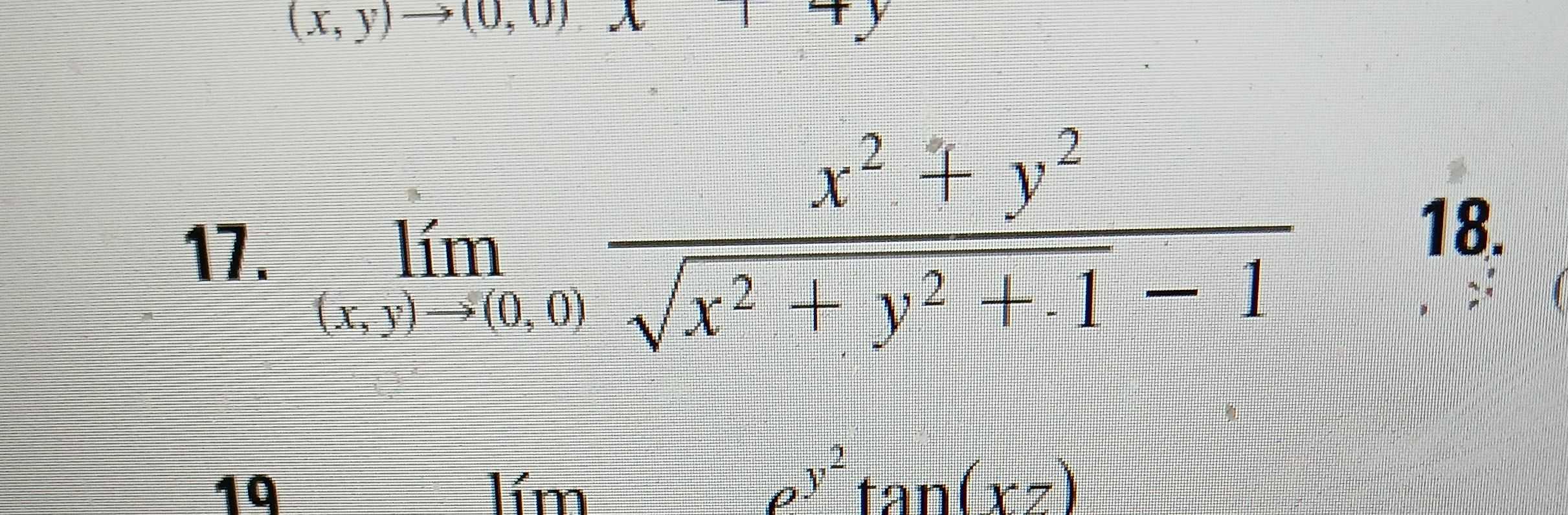AI tutor
Full solution
Q.
- Substitute : Step : Simplify the expression by substituting for , where is the distance from the origin in polar coordinates.- Calculation: Let .- Reasoning: This substitution simplifies the expression to a function of a single variable .-
- Rewrite using : Step : Rewrite the limit using .- Calculation: .- Reasoning: This step converts the two-variable limit into a one-variable limit, making it easier to evaluate.-
- Apply L'Hopital's Rule: Step : Apply L'Hopital's Rule since direct substitution gives , an indeterminate form.- Calculation: Differentiate the numerator and the denominator with respect to . Numerator derivative: . Denominator derivative: .- Reasoning: L'Hopital's Rule is used to resolve indeterminate forms by differentiating the numerator and denominator.
- Simplify after differentiation: Step : Simplify the expression after differentiation.- Calculation: .- Reasoning: Simplifying the derivatives to find the new limit.-
- Simplify and evaluate: Step : Simplify further and evaluate the limit.- Calculation: .- Reasoning: Cancel from numerator and denominator.-
- Final simplification: Step : Final simplification and evaluation.- Calculation: .- Reasoning: After canceling , the limit depends only on the remaining terms.-