AI tutor
Full solution
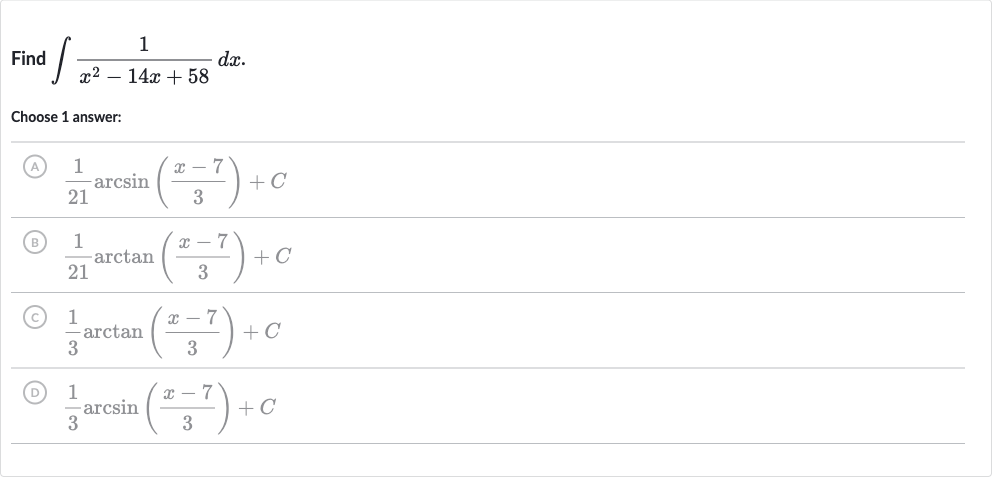
Q. Find .Choose answer:(A) (B) (C) (D)
- Complete the Square: First, let's complete the square for the denominator . So, the integral becomes .
- Use Substitution: Now, let's use a substitution to make it look like the arctan derivative.Let , then , so .
- Substitute and : Substitute and into the integral.
- Simplify the Integral: Simplify the integral. .
- Recognize Integral: Recognize that the integral of is . So, .
- Substitute back: Substitute back in terms of .arctan() + = arctan + .