AI tutor
Full solution
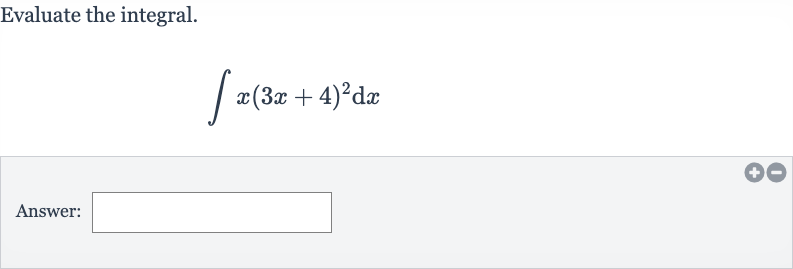
Q. Evaluate the integral.Answer:
- Substitution Method: Let's use substitution to solve the integral. We will let , then . We need to express in terms of and in terms of .
- Express in terms of : First, we solve for in terms of : implies .
- Express in terms of : Next, we express in terms of : since , we have .
- Substitute and : Now we substitute and in the integral: becomes .
- Simplify the integral: Simplify the integral: \int \left(\frac{u - \(4\)}{\(3\)}\right)u^\(2\left(\frac{du}{}\right) = \frac{}{}\int u^(u - ) du = \frac{}{}\int (u^ - u^) du.
- Find the antiderivative: Find the antiderivative: .
- Simplify the antiderivative: Simplify the antiderivative: (\frac{\(1\)}{\(9\)})\left(\frac{u^\(4\)}{\(4\)} - \frac{\(4\)u^\(3\)}{\(3\)}\right) + C = \left(\frac{\(1\)}{\(36\)}\right)u^\(4 - \left(\frac{}{}\right)u^ + C.
- Substitute back for u: Substitute back for u: .