Full solution
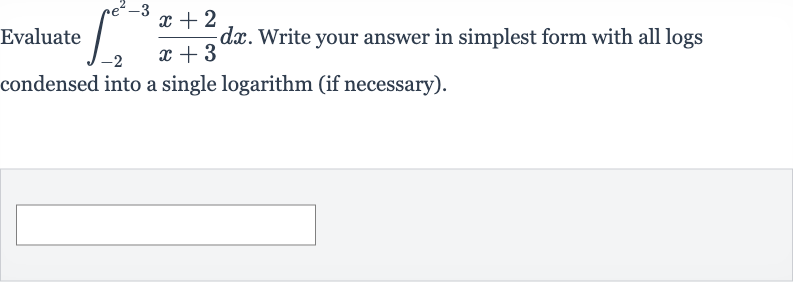
Q. Evaluate . Write your answer in simplest form with all logs condensed into a single logarithm (if necessary).
- Identify Integral: Identify the integral to be solved.We need to evaluate the integral of the function within the limits of integration from to .
- Simplify Integrand: Simplify the integrand if possible.The integrand can be rewritten as by dividing each term in the numerator by the denominator.
- Split Integral: Split the integral into two simpler integrals.The integral of the sum of two functions is the sum of their integrals. Therefore, we can write:
- Evaluate First Integral: Evaluate the first integral.The integral of with respect to is . So, .
- Evaluate Second Integral: Evaluate the second integral.The integral of with respect to is . So, .
- Combine Results: Combine the results of the two integrals. The combined result of the integrals is .
- Apply Limits: Apply the limits of integration.We need to evaluate from to .
- Calculate Definite Integral: Calculate the definite integral. Now, we subtract from :
- Simplify Expression: Simplify the expression.Since and , we have:
- Write Final Answer: Write the final answer.The final value of the integral is .