Full solution
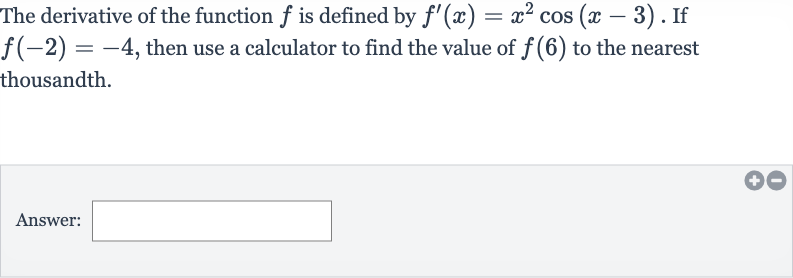
Q. The derivative of the function is defined by . If , then use a calculator to find the value of to the nearest thousandth.Answer:
- Integrate : To find the value of , we need to integrate the derivative to get the original function . We will then use the initial condition to find the constant of integration.
- Apply integration by parts: Integrate with respect to . This requires integration by parts or a special technique since it is a product of a polynomial and a trigonometric function.
- Simplify and integrate: Let , which means . Let , which means . Now we can apply integration by parts: .
- Use initial condition: Using integration by parts, we get . The second integral also requires integration by parts.
- Calculate trigonometric values: Let , which means . Let , which means . Apply integration by parts again: .
- Find constant of integration: We get . Simplify and integrate the remaining term.
- Find : Simplifying, we have . The last integral is straightforward: .
- Find : Simplifying, we have . The last integral is straightforward: .Putting it all together, we have , where is the constant of integration.
- Find : Simplifying, we have . The last integral is straightforward: .Putting it all together, we have , where is the constant of integration.Now we use the initial condition to solve for . Plug in into the equation: .
- Find : Simplifying, we have . The last integral is straightforward: . Putting it all together, we have , where is the constant of integration. Now we use the initial condition to solve for . Plug in into the equation: . Calculate the trigonometric values and simplify: . Use a calculator to find the values of and .
- Find : Simplifying, we have . The last integral is straightforward: . Putting it all together, we have , where is the constant of integration. Now we use the initial condition to solve for . Plug in into the equation: . Calculate the trigonometric values and simplify: . Use a calculator to find the values of and . After calculating, we find that and . Now substitute these values into the equation: .
- Find : Simplifying, we have . The last integral is straightforward: .Putting it all together, we have , where is the constant of integration.Now we use the initial condition to solve for . Plug in into the equation: .Calculate the trigonometric values and simplify: . Use a calculator to find the values of and .After calculating, we find that and . Now substitute these values into the equation: .Simplify the equation to find : . Now solve for : .
- Find : Simplifying, we have . The last integral is straightforward: . Putting it all together, we have , where is the constant of integration. Now we use the initial condition to solve for . Plug in into the equation: . Calculate the trigonometric values and simplify: . Use a calculator to find the values of and . After calculating, we find that and . Now substitute these values into the equation: . Simplify the equation to find : . Now solve for : . Calculate the value of : . This is the constant of integration.
- Find : Simplifying, we have . The last integral is straightforward: . Putting it all together, we have , where is the constant of integration. Now we use the initial condition to solve for . Plug in into the equation: . Calculate the trigonometric values and simplify: . Use a calculator to find the values of and . After calculating, we find that and . Now substitute these values into the equation: . Simplify the equation to find : . Now solve for : . Calculate the value of : . This is the constant of integration. Now that we have , we can find by plugging into the integrated function: .
- Find : Simplifying, we have . The last integral is straightforward: . Putting it all together, we have , where is the constant of integration. Now we use the initial condition to solve for . Plug in into the equation: . Calculate the trigonometric values and simplify: . Use a calculator to find the values of and . After calculating, we find that and . Now substitute these values into the equation: . Simplify the equation to find : . Now solve for : . Calculate the value of : . This is the constant of integration. Now that we have , we can find by plugging into the integrated function: . Calculate the trigonometric values for and using a calculator, then substitute them into the equation to find .
- Find : Simplifying, we have . The last integral is straightforward: . Putting it all together, we have , where is the constant of integration. Now we use the initial condition to solve for . Plug in into the equation: . Calculate the trigonometric values and simplify: . Use a calculator to find the values of and . After calculating, we find that and . Now substitute these values into the equation: . Simplify the equation to find : . Now solve for : . Calculate the value of : . This is the constant of integration. Now that we have , we can find by plugging into the integrated function: . Calculate the trigonometric values for and using a calculator, then substitute them into the equation to find . After calculating, we find that and . Now substitute these values into the equation: .
- Find : Simplifying, we have . The last integral is straightforward: . Putting it all together, we have , where is the constant of integration. Now we use the initial condition to solve for . Plug in into the equation: . Calculate the trigonometric values and simplify: . Use a calculator to find the values of and . After calculating, we find that and . Now substitute these values into the equation: . Simplify the equation to find : . Now solve for : . Calculate the value of : . This is the constant of integration. Now that we have , we can find by plugging into the integrated function: . Calculate the trigonometric values for and using a calculator, then substitute them into the equation to find . After calculating, we find that and . Now substitute these values into the equation: . Simplify the equation to find : . Now calculate the sum to get the value of .
- Find : Simplifying, we have . The last integral is straightforward: . Putting it all together, we have , where is the constant of integration. Now we use the initial condition to solve for . Plug in into the equation: . Calculate the trigonometric values and simplify: . Use a calculator to find the values of and . After calculating, we find that and . Now substitute these values into the equation: . Simplify the equation to find : . Now solve for : . Calculate the value of : . This is the constant of integration. Now that we have , we can find by plugging into the integrated function: . Calculate the trigonometric values for and using a calculator, then substitute them into the equation to find . After calculating, we find that and . Now substitute these values into the equation: . Simplify the equation to find : . Now calculate the sum to get the value of . Calculate the value of : . Round to the nearest thousandth.
- Find : Simplifying, we have . The last integral is straightforward: .Putting it all together, we have , where is the constant of integration.Now we use the initial condition to solve for . Plug in into the equation: .Calculate the trigonometric values and simplify: . Use a calculator to find the values of and .After calculating, we find that and . Now substitute these values into the equation: .Simplify the equation to find : . Now solve for : .Calculate the value of : . This is the constant of integration.Now that we have , we can find by plugging into the integrated function: .Calculate the trigonometric values for and using a calculator, then substitute them into the equation to find .After calculating, we find that and . Now substitute these values into the equation: .Simplify the equation to find : . Now calculate the sum to get the value of .Calculate the value of : . Round to the nearest thousandth.The value of to the nearest thousandth is approximately .
More problems from Find roots using a calculator
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help