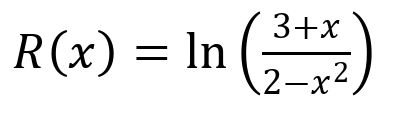AI tutor
Full solution
Q.
- Identify Function: Identify the function that we need to differentiate.We need to find , the derivative of with respect to .
- Apply Chain Rule: Apply the chain rule for differentiation to the natural logarithm function. The derivative of with respect to is , where is a function of . In this case, .
- Differentiate Numerator and Denominator: Differentiate the numerator and the denominator of separately.The derivative of the numerator, , with respect to is .The derivative of the denominator, , with respect to is .
- Apply Quotient Rule: Apply the quotient rule to differentiate .The quotient rule is given by , where is the numerator and is the denominator.
- Perform Quotient Rule Calculations: Perform the calculations for the quotient rule.Let and . and .Now, apply the quotient rule: .
- Simplify Expression: Simplify the expression obtained from the quotient rule. .
- Expand and Combine Terms: Expand and combine like terms in the numerator. .Combine like terms: .
- Write Final Derivative Expression: Write the final expression for the derivative of ..This is the derivative of the function with respect to .
More problems from Evaluate rational exponents
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help