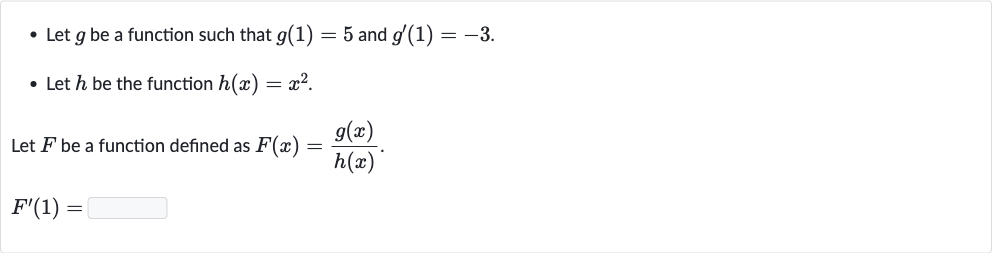Full solution
Q. - Let be a function such that and .- Let be the function .Let be a function defined as .
- Given values: We are given and . We also know that , so and , so .
- Quotient rule for derivatives: To find , we need to use the quotient rule for derivatives, which states that if , then .
- Substitute values into formula: Now we substitute into the quotient rule formula using the values we have: , , , and ..
More problems from Find the vertex of the transformed function
QuestionGet tutor help