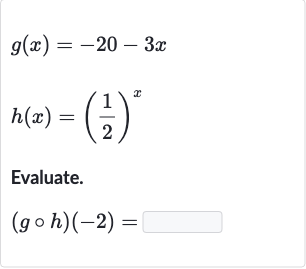AI tutor
Full solution
Q. Evaluate.
- Understand Function Composition: Understand the composition of functions. The composition of two functions means we first apply to , and then apply to the result of .
- Evaluate : Evaluate .
- Evaluate : Evaluate .Now we need to apply to the result from Step , which is .
- Combine Results: Combine the results to find .
More problems from Compare linear and exponential growth
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help