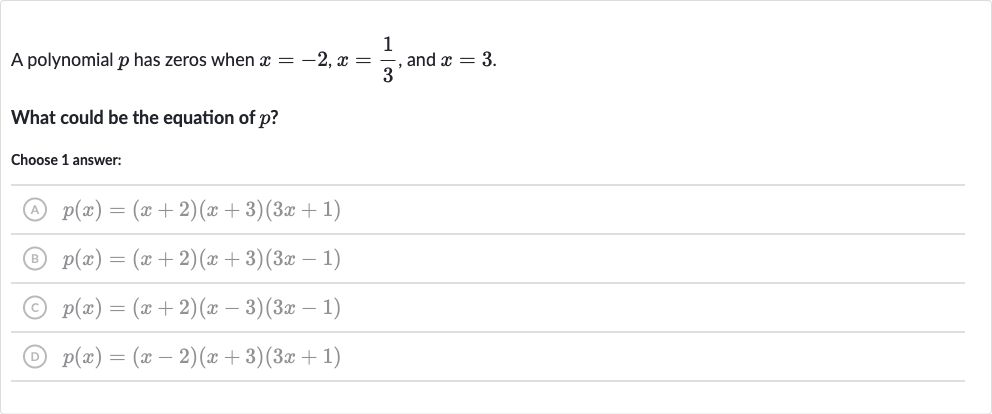Full solution
Q. A polynomial has zeros when , and .What could be the equation of ?Choose answer:(A) (B) (C) (D)
- Identify Zeros: Zeros are , , and . The factors of will be , , and .
- Eliminate Fraction: To get rid of the fraction in the second factor, multiply by to get which simplifies to .
- Formulate Equation: The equation of is .
- Match with Options: Match the equation with the given options. The correct option is (C) .
More problems from Write a quadratic function from its x-intercepts and another point
QuestionGet tutor help