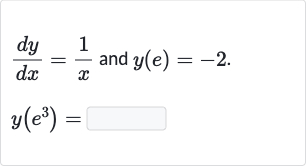AI tutor
Full solution
Q. and .
- Integrate and solve equation: Integrate both sides of the equation to find .
- Find constant using initial condition: Substitute to find the constant using the initial condition .
- Write general solution: Write the general solution for with the found constant .
- Substitute : Substitute into the general solution to find .
- Simplify expression: Simplify the expression since .
- Calculate final value: Calculate the final value of .