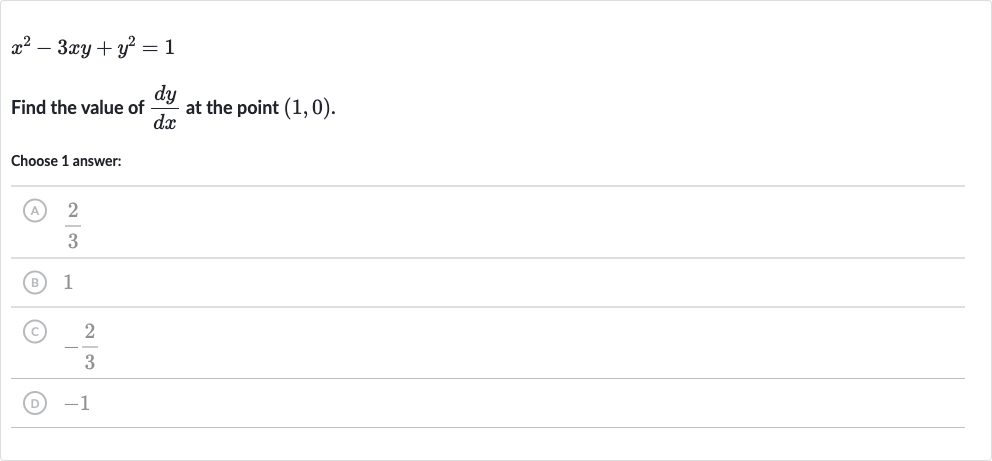
Full solution
Q. Find the value of at the point .Choose answer:(A) (B) (C) (D)
- Differentiate Equation Implicitly: Implicitly differentiate both sides of the equation with respect to .
- Apply Product Rule for : Use the product rule for : . So,
- Differentiate and : Differentiate to get and to get .
- Solve for : Rearrange the terms to solve for .
- Factor out dy/dx: Factor out on the right side.
- Isolate : Divide both sides by to isolate .
- Plug in Point: Plug in the point into the equation.
- Simplify Equation: Simplify the equation.
- Calculate Final Value: Calculate the final value.