Full solution
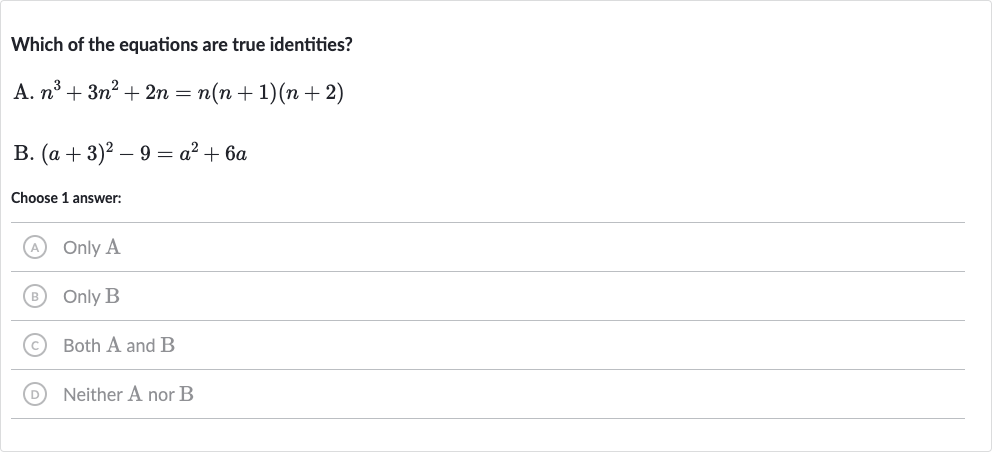
Q. Which of the equations are true identities?A. B. Choose answer:(A) Only A(B) Only B(C) Both and (D) Neither A nor B
- Expand Equation A: Let's expand the right side of equation A and see if it matches the left side.
- Check Equation B: Now let's check equation B by expanding the left side.
- Verify Identities: Both equations and seem to be true identities after expanding and simplifying.