AI tutor
Full solution
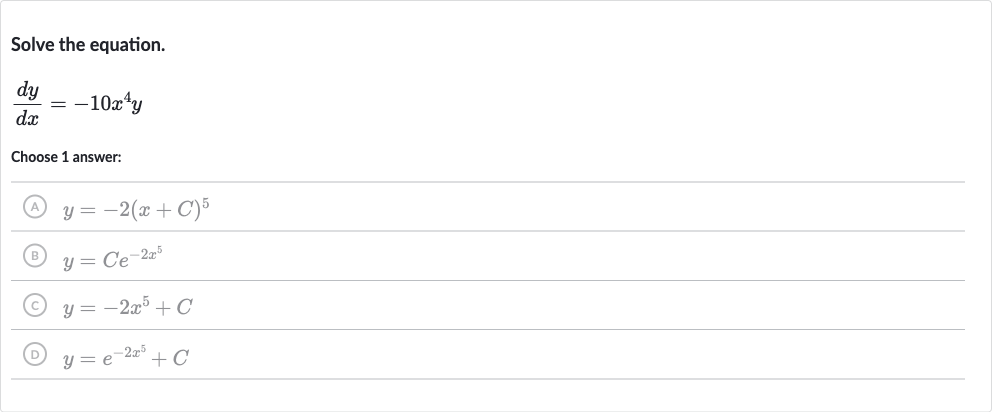
Q. Solve the equation.Choose answer:(A) (B) (C) (D)
- Separate variables: We are given a first-order separable differential equation . To solve it, we need to separate the variables and on different sides of the equation.
- Rewrite equation: Rewrite the equation to separate the variables: .
- Integrate both sides: Integrate both sides of the equation. The left side with respect to and the right side with respect to .
- Exponentiate both sides: The integral of dy is , and the integral of dx is . Don't forget to add the constant of integration on one side..
- Solve for : To solve for , we exponentiate both sides of the equation to get rid of the natural logarithm.
- Final solution: Since is just and is a constant which we can call , we have:.
- Final solution: Since is just and is a constant which we can call , we have:.Since can be positive or negative, we can drop the absolute value to get:.However, since the constant can absorb the sign, we can write:.