AI tutor
Full solution
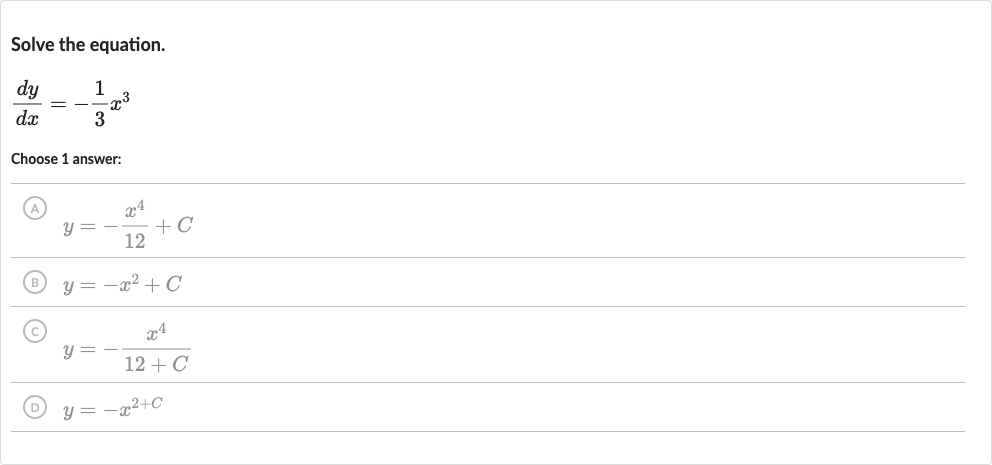
Q. Solve the equation.Choose answer:(A) (B) (c) (D)
- Integrate with respect to : To solve the differential equation , we need to integrate both sides with respect to .
- Apply power rule for integration: The antiderivative of with respect to is found using the power rule for integration, which states that the integral of with respect to is , where is the constant of integration.
- Antiderivative of : Applying the power rule to , we get:
- Simplify the expression: Simplifying the expression, we get:
- Final antiderivative: Therefore, the antiderivative of is , which corresponds to answer choice .