AI tutor
Full solution
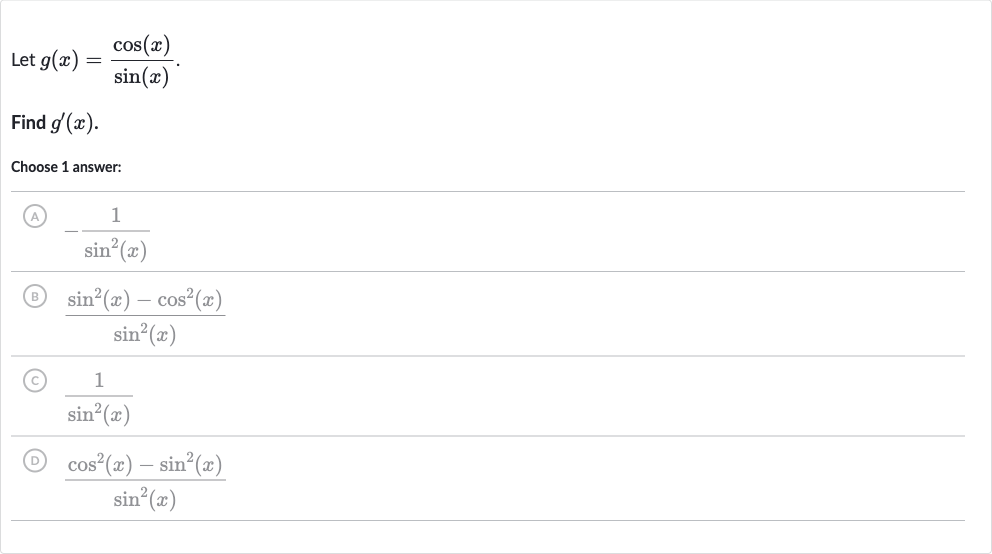
Q. Let .Find .Choose answer:(A) (B) (C) (D)
- Recognize Function Type: Recognize that is a quotient of two functions, where the numerator is and the denominator is . To find the derivative , we will use the quotient rule.
- Apply Quotient Rule: The quotient rule states that if we have a function , then its derivative is given by . Here, and .
- Find Derivative of Cos(x): Find the derivative of the numerator . The derivative of with respect to is .
- Find Derivative of Sin(x): Find the derivative of the denominator . The derivative of with respect to is .
- Apply Quotient Rule: Apply the quotient rule using the derivatives from steps and . So, .
- Simplify Expression: Simplify the expression for . We have .
- Apply Pythagorean Identity: Recognize that , which is the Pythagorean identity. Therefore, .
- Substitute Identity: Substitute the Pythagorean identity into the expression for to get .
- Final Simplified Form: The final simplified form of is , which corresponds to answer choice (A).