AI tutor
Full solution
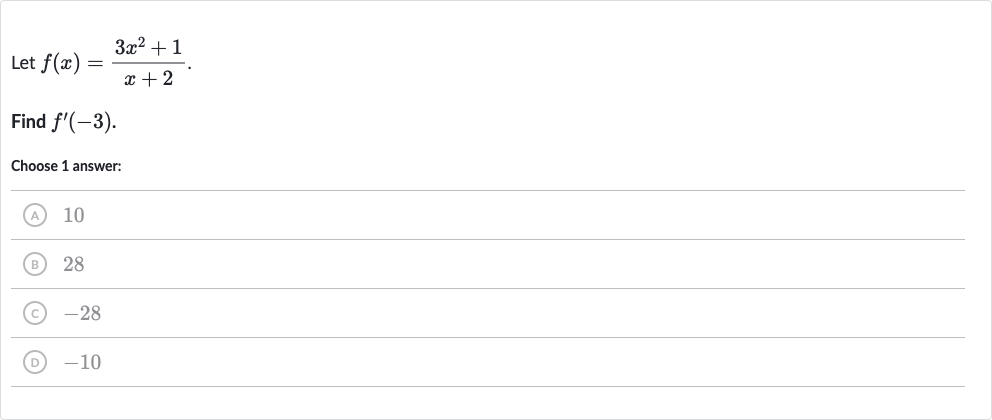
Q. Let .Find .Choose answer:(A) (B) (C) (D)
- Quotient Rule Application: To find the derivative of the function , we will use the quotient rule which states that if , then . Here, and .
- Derivative of : First, we find the derivative of . Using the power rule, we get .
- Derivative of : Next, we find the derivative of . The derivative of a constant is , and the derivative of with respect to is , so .
- Applying Quotient Rule: Now we apply the quotient rule: .
- Simplifying Numerator: We simplify the numerator: .
- Evaluate at : Now we have . We need to evaluate this derivative at .
- Calculate Numerator: Substitute into the derivative: .
- Calculate Denominator: Calculate the numerator: .
- Final Result: Calculate the denominator: .
- Final Result: Calculate the denominator: .Now we have .