AI tutor
Welcome to Bytelearn!
Let’s check out your problem:
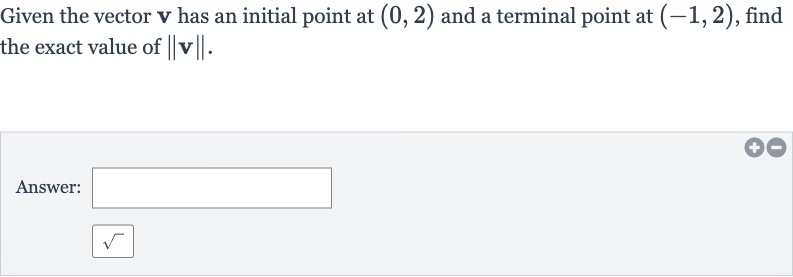
Given the vector has an initial point at and a terminal point at , find the exact value of .Answer:
Full solution
Q. Given the vector has an initial point at and a terminal point at , find the exact value of .Answer:
- Calculate Distance Formula: To find the magnitude of vector , we need to calculate the distance between its initial and terminal points using the distance formula for points in a D space: , where is the initial point and is the terminal point.
- Substitute Coordinates: Substitute the coordinates of the initial point and the terminal point into the distance formula: .
- Calculate Squares: Calculate the squares of the differences: .
- Simplify Squares: Simplify the squares: .
- Add Values: Add the values inside the square root:
- Take Square Root: Take the square root of : .
More problems from Transformations of absolute value functions: translations and reflections
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
