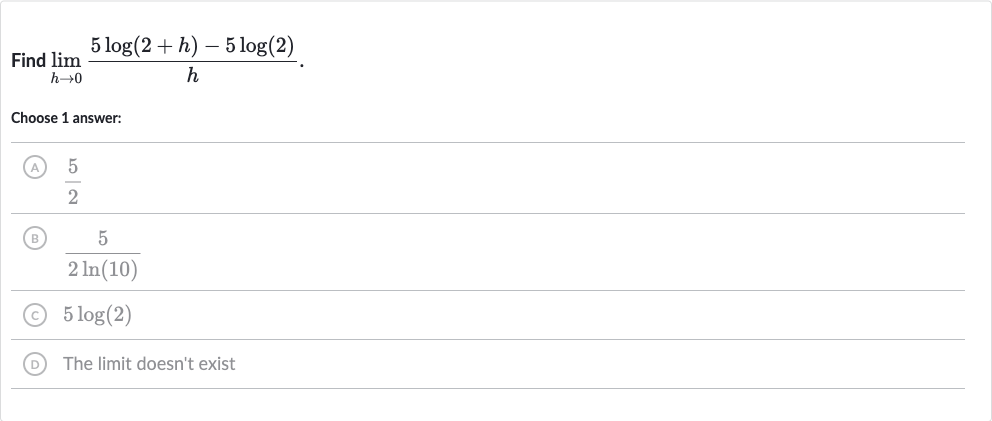
Full solution
Q. Find .Choose answer:(A) (B) (C) (D) The limit doesn't exist
- Combine logarithmic terms: Use the properties of logarithms to combine the terms in the numerator.
- Apply constant multiple rule: Apply the constant multiple rule in limits to take the constant out of the limit.
- Use derivative definition: Use the definition of the derivative for the function at . where
- Calculate derivative: The derivative of is . So, .
- Multiply by constant: Multiply the derivative by the constant that we factored out earlier.