AI tutor
Full solution
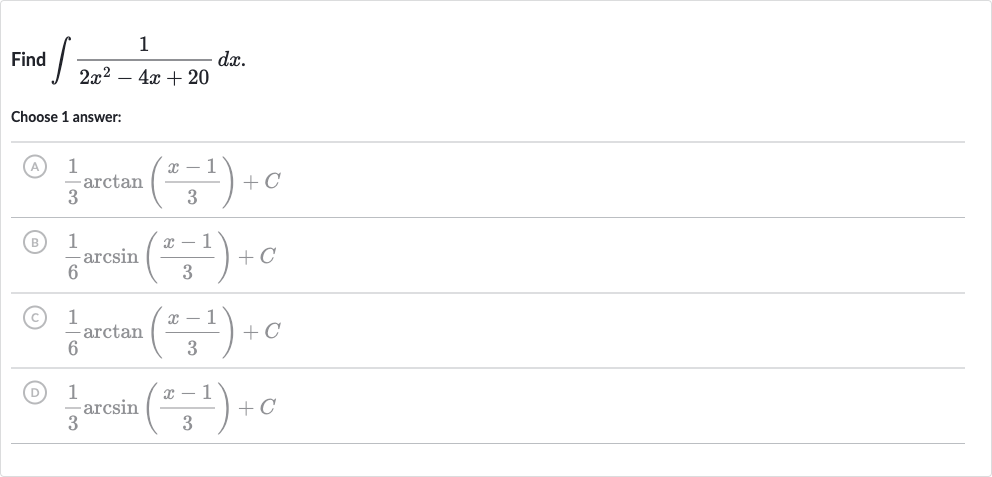
Q. Find .Choose answer:(A) (B) (C) (D)
- Complete the Square: First, complete the square for the quadratic in the denominator.Now, to complete the square, we need to add and subtract where is the coefficient of .So, .Add and subtract inside the parenthesis and factor out the .
- Rewrite the Integral: Now, rewrite the integral with the completed square.Simplify the integral by taking out the constant.
- Recognize Arctan Formula: Recognize the integral as a form of the inverse tangent function, , where the integral of is . Here, and , so .
- Apply Arctan Formula: Apply the arctan formula.Simplify the constants.