AI tutor
Full solution
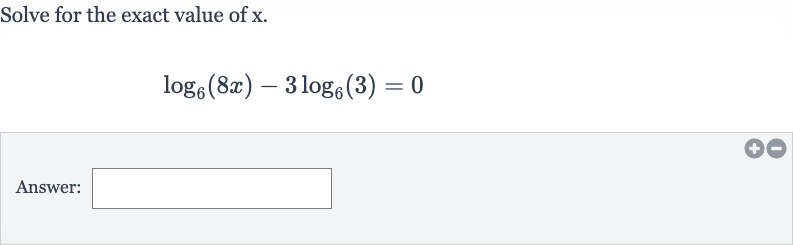
Q. Solve for the exact value of .Answer:
- Apply Power Rule: Apply the power rule of logarithms to simplify the equation.The power rule states that , where is a constant, is the base of the logarithm, and is the argument of the logarithm. We can apply this rule to the term to simplify the equation.
- Combine Logarithmic Terms: Combine the logarithmic terms using the quotient rule.The quotient rule states that , where is the base of the logarithm, and are the arguments of the logarithm. We can combine the two logarithmic terms into a single logarithm.
- Convert to Exponential: Convert the logarithmic equation to an exponential equation.The definition of a logarithm states that if , then . We can use this definition to convert the logarithmic equation into an exponential equation.
- Solve for x: Solve for x.Since , we can multiply both sides of the equation by to solve for .