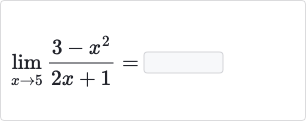AI tutor
Full solution
Q.
- Substitute : Substitute the value of with in the expression to see if the limit can be directly evaluated.Substitute :
- Perform calculations: Perform the calculations after substitution.= =
- Check determinate form: Check if the result is a determinate form or if there are any indeterminate forms such as or .Since the result is a real number and not an indeterminate form, the limit can be evaluated directly.
- Conclude the limit: Conclude the limit based on the calculations.The limit of as approaches is .
More problems from Negative Exponents
QuestionGet tutor help