AI tutor
Full solution
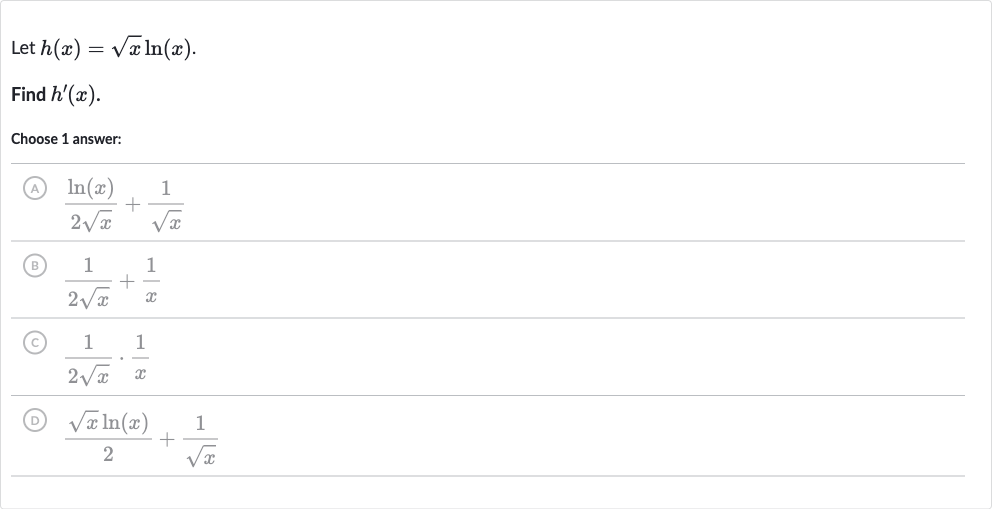
Q. Let .Find .Choose answer:(A) (B) (C) (D)
- Define Functions: The product rule states that . Let and . We need to find and .
- Find : Differentiate . We can write as and use the power rule. .
- Find : Differentiate . The derivative of is . So, .
- Apply Product Rule: Now apply the product rule: . Plug in the derivatives we found: .
- Simplify Expression: Simplify the expression: . This is because .
More problems from Multiplication with rational exponents
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help