Full solution
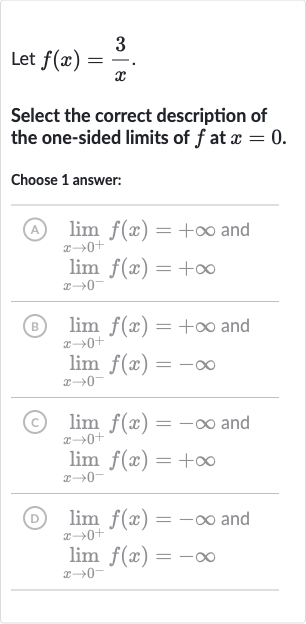
Q. Let .Select the correct description of the one-sided limits of at .Choose answer:(A) and (B) and (C) and (D) and
- Evaluate positive limit: Evaluate the one-sided limit of as approaches from the positive side ().As approaches from the positive side, the value of becomes very large because we are dividing a constant by a very small positive number. Therefore, the limit is positive infinity.
- Evaluate negative limit: Evaluate the one-sided limit of as approaches from the negative side ().As approaches from the negative side, the value of becomes very large in the negative direction because we are dividing a constant by a very small negative number. Therefore, the limit is negative infinity.
- Combine results: Combine the results from the previous steps to select the correct description of the one-sided limits of at . From step , we have . From step , we have . Therefore, the correct answer is (B) and .