AI tutor
Welcome to Bytelearn!
Let’s check out your problem:
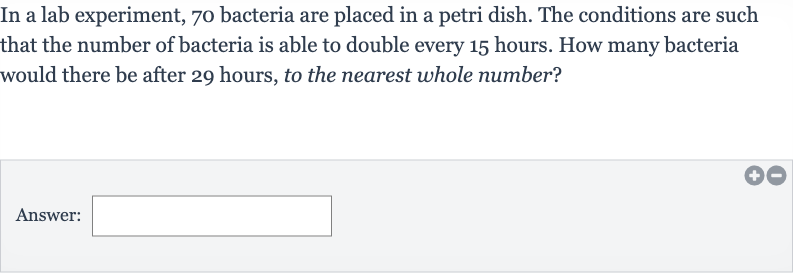
In a lab experiment, bacteria are placed in a petri dish. The conditions are such that the number of bacteria is able to double every hours. How many bacteria would there be after hours, to the nearest whole number?Answer:
Full solution
Q. In a lab experiment, bacteria are placed in a petri dish. The conditions are such that the number of bacteria is able to double every hours. How many bacteria would there be after hours, to the nearest whole number?Answer:
- Determine Doubling Periods: First, we need to determine how many times the bacteria population can double in hours. Since the bacteria double every hours, we divide the total time by the doubling period. hours hours per doubling period = doubling periods.
- Calculate Full Periods: Since the bacteria can only double an integer number of times, we need to consider how many full doubling periods occur within hours. We can't have a fraction of a doubling period, so we take the floor of the previous result.Full doubling periods = (since indicates that only one full doubling period has occurred within hours).
- Calculate After Period: Now we calculate the number of bacteria after one full doubling period. We start with bacteria and double it once.Number of bacteria after doubling period = bacteria.
- Estimate Growth: We have hours remaining after the first doubling period ( hours - hours = hours). We need to estimate the growth during this period. Since the bacteria double every hours, we can use the fraction of the doubling period that has passed () to estimate the growth.Fraction of doubling period passed = .
- Calculate Growth Factor: We calculate the growth factor for the remaining hours using the fraction of the doubling period.Growth factor for hours = .
- Apply Growth Factor: Now we apply the growth factor to the number of bacteria after the first doubling period to estimate the total number of bacteria after hours.Estimated number of bacteria after hours .
- Calculate Estimated Bacteria: We perform the calculation for the growth factor and then multiply by the number of bacteria after the first doubling period. (rounded to three decimal places for simplicity).Estimated number of bacteria after hours .
- Round to Nearest Whole: Finally, we calculate the estimated number of bacteria to the nearest whole number.Estimated number of bacteria after hours .Since we need to report the number of bacteria to the nearest whole number, we round to .
More problems from Convert between customary and metric systems
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
