AI tutor
Full solution
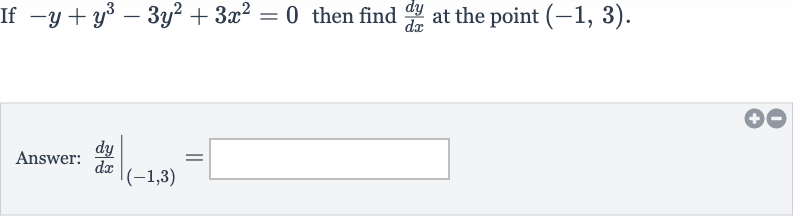
Q. If then find at the point .Answer:
- Implicit Differentiation: To find the derivative , we need to implicitly differentiate the given equation with respect to . The equation is .
- Chain Rule Application: Differentiate each term with respect to . For terms with , we use the chain rule, treating as a function of (). The derivative of with respect to is . The derivative of with respect to is by the chain rule. The derivative of with respect to is by the chain rule. The derivative of with respect to is .
- Grouping Terms: Writing the derivatives out, we get: .
- Factor Out : Now we group the terms with on one side and the term with on the other side:.
- Solve for : Factor out from the left side of the equation:.
- Substitute Values: Solve for by dividing both sides by :.
- Calculate Denominator: Now we need to evaluate at the point . Substitute and into the equation:.
- Calculate Numerator: Calculate the denominator:.
- Divide to Find : Calculate the numerator:.
- Simplify Fraction: Now, divide the numerator by the denominator to find at the point :
- Simplify Fraction: Now, divide the numerator by the denominator to find at the point :
. Simplify the fraction:
.