AI tutor
Full solution
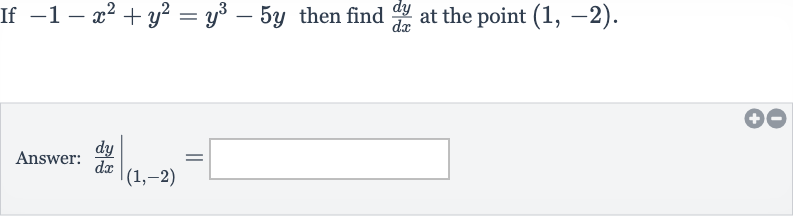
Q. If then find at the point .Answer:
- Implicit Differentiation: First, we need to implicitly differentiate both sides of the equation with respect to . The equation is . Differentiating both sides with respect to gives us: .
- Differentiate Left Side: Differentiate the left side of the equation term by term. because the derivative of a constant is . because the derivative of is , and we multiply by the coefficient . because is a function of , so we use the chain rule.The left side becomes .
- Differentiate Right Side: Differentiate the right side of the equation term by term. because we use the chain rule, where the derivative of is , and we multiply by . because the derivative of with respect to is times the derivative of with respect to .The right side becomes .
- Combine Derivatives: Combine the derivatives to form an equation:.Now we need to solve for .
- Group and Factor: Group all the terms containing on one side and the remaining terms on the other side:.Factor out from the left side:.
- Solve for : Solve for by dividing both sides by :
- Substitute Point: Substitute the point into the equation to find at that point:$(dy/dx)|_{(\(1\),\(-2\))} = \frac{\(2\)(\(1\))}{\(2\)(\(-2\)) - \(3\)(\(-2\))^\(2\) + \(5\)}.
- Calculate \(\frac{dy}{dx}\): Calculate the value of \(\left(\frac{dy}{dx}\right)\) at the point \((1, -2)\):
\(\left.\frac{dy}{dx}\right|_{(1,-2)} = \frac{2}{(-4 - 3(4) + 5)}\).
\(\left.\frac{dy}{dx}\right|_{(1,-2)} = \frac{2}{(-4 - 12 + 5)}\).
\(\left.\frac{dy}{dx}\right|_{(1,-2)} = \frac{2}{(-11)}\).
\(\left.\frac{dy}{dx}\right|_{(1,-2)} = -\frac{2}{11}\).