AI tutor
Full solution
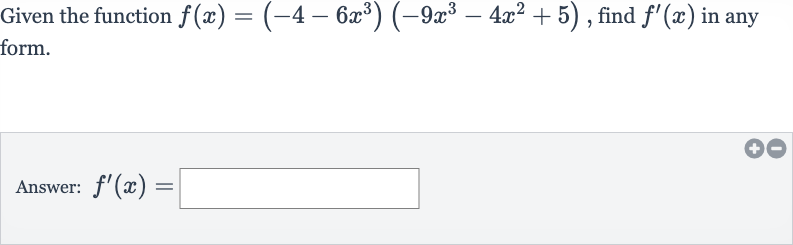
Q. Given the function , find in any form.Answer:
- Apply Product Rule: To find the derivative of the function , we will use the product rule. The product rule states that the derivative of a product of two functions is the derivative of the first function times the second function plus the first function times the derivative of the second function.
- Find Derivatives: Let's denote the first function as and the second function as . We need to find the derivatives and .
- Distribute Terms: First, we find the derivative of . The derivative of a constant is , and the derivative of is . So, .
- Simplify Expressions: Next, we find the derivative of . The derivative of is , the derivative of is , and the derivative of a constant is . So, .
- Combine Like Terms: Now we apply the product rule: . Substituting the derivatives we found, we get .
- Combine Like Terms: Now we apply the product rule: . Substituting the derivatives we found, we get .We need to distribute the terms in the expression . Let's do this step by step.
- Combine Like Terms: Now we apply the product rule: . Substituting the derivatives we found, we get .We need to distribute the terms in the expression . Let's do this step by step.First, distribute across the terms in the first parenthesis: .
- Combine Like Terms: Now we apply the product rule: . Substituting the derivatives we found, we get .We need to distribute the terms in the expression . Let's do this step by step.First, distribute across the terms in the first parenthesis: .Now, distribute and across the terms in the second parenthesis: .
- Combine Like Terms: Now we apply the product rule: . Substituting the derivatives we found, we get .We need to distribute the terms in the expression . Let's do this step by step.First, distribute across the terms in the first parenthesis: .Now, distribute and across the terms in the second parenthesis: .Let's simplify the terms we have so far: .
- Combine Like Terms: Now we apply the product rule: . Substituting the derivatives we found, we get .We need to distribute the terms in the expression . Let's do this step by step.First, distribute across the terms in the first parenthesis: .Now, distribute and across the terms in the second parenthesis: .Let's simplify the terms we have so far: .Combine like terms to get the final derivative: .
- Combine Like Terms: Now we apply the product rule: . Substituting the derivatives we found, we get .We need to distribute the terms in the expression . Let's do this step by step.First, distribute across the terms in the first parenthesis: .Now, distribute and across the terms in the second parenthesis: .Let's simplify the terms we have so far: .Combine like terms to get the final derivative: .After combining like terms, we get .