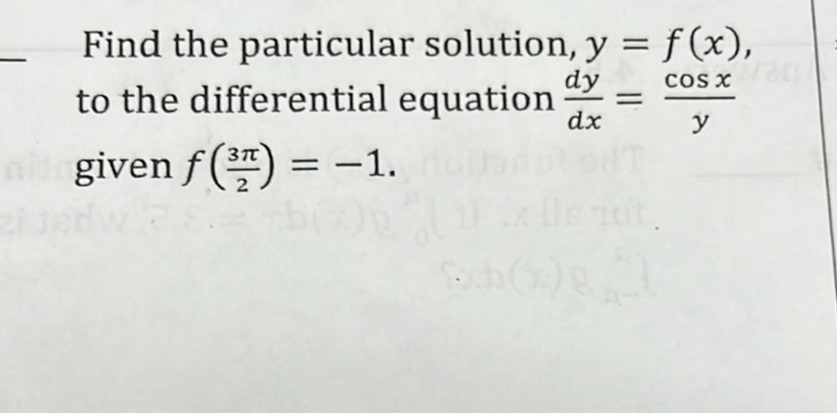Full solution
Q. Find the particular solution, , to the differential equation given
- Separate and Integrate: Step : Separate variables and integrate.We start by separating the variables in the differential equation . Rearrange to get . Now, integrate both sides:
- Solve for y: Step : Solve for y.To find y, we take the square root of both sides:
- Find with Initial Condition: Step : Use the initial condition to find . We know that . Plugging into : Since , Squaring both sides gives:
- Write Particular Solution: Step : Write the particular solution.With , the solution becomes:Since we need the solution that passes through and we calculated earlier:The correct sign is negative, so: