AI tutor
Full solution
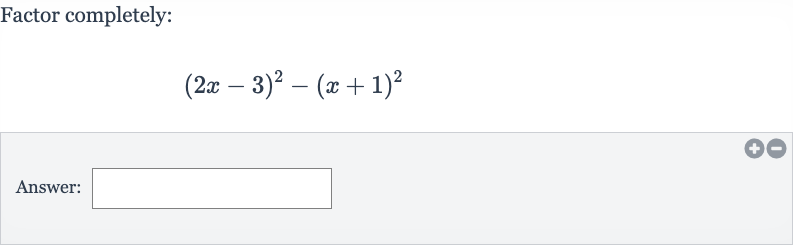
Q. Factor completely:Answer:
- Recognize as difference of squares: Recognize the expression as a difference of squares.The given expression is in the form of , which is a difference of squares. and Difference of squares formula:
- Apply formula: Apply the difference of squares formula.Using the formula from Step , we can write the expression as:
- Simplify terms: Simplify the terms inside the parentheses.Simplify the first set of parentheses:Simplify the second set of parentheses:
- Write final form: Write the final factored form.The completely factored form of the expression is:
More problems from Powers with negative bases
QuestionGet tutor help