AI tutor
Full solution
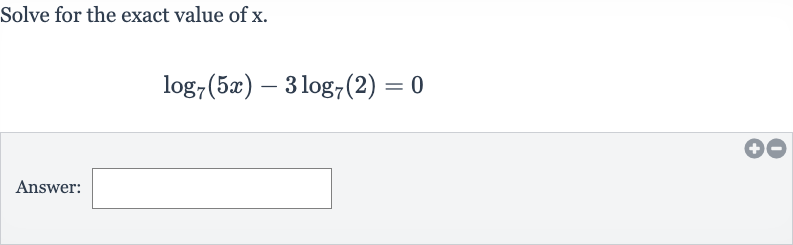
Q. Solve for the exact value of .Answer:
- Apply Power Rule: Apply the power rule of logarithms to simplify the term with the coefficient.The power rule of logarithms states that . Let's apply this to the term .Power rule application: Calculation:
- Rewrite Equation: Rewrite the original equation using the result from Step .The original equation becomes .
- Apply Quotient Rule: Apply the quotient rule of logarithms to combine the logarithms into a single logarithm.The quotient rule of logarithms states that . Let's apply this to combine the logarithms.Quotient rule application:
- Set Equal to Base: Set the argument of the logarithm equal to the base raised to the power of the other side of the equation.Since , we can write this as .Calculation:
- Solve for x: Solve for x.We have the equation . Multiply both sides by to isolate .Calculation:
- Complete Calculation: Complete the calculation to find the value of .Calculation: Divide both sides by to solve for .Calculation: