AI tutor
Full solution
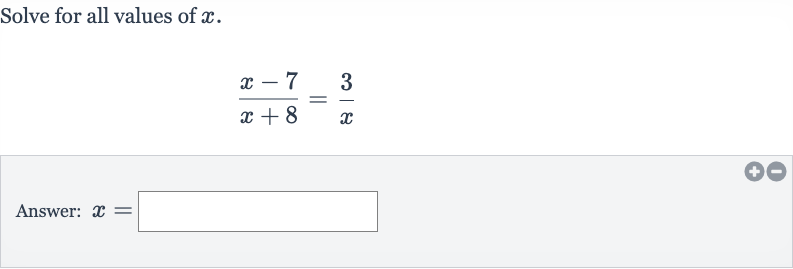
Q. Solve for all values of .Answer:
- Cross-multiply fractions: Cross-multiply to eliminate the fractions.
- Distribute and simplify: Distribute to simplify both sides of the equation.
- Move terms and set to zero: Move all terms to one side to set the equation to zero.
- Factor quadratic equation: Factor the quadratic equation.
- Solve for : Set each factor equal to zero and solve for . or or
- Check for extraneous solutions: Check for extraneous solutions by plugging the values back into the original equation.For : (True, so is a valid solution)For : (True, but is not a valid solution because it makes the denominator of the original equation's right side zero)
More problems from Solve multi-step equations with fractional coefficients
QuestionGet tutor help