AI tutor
Full solution
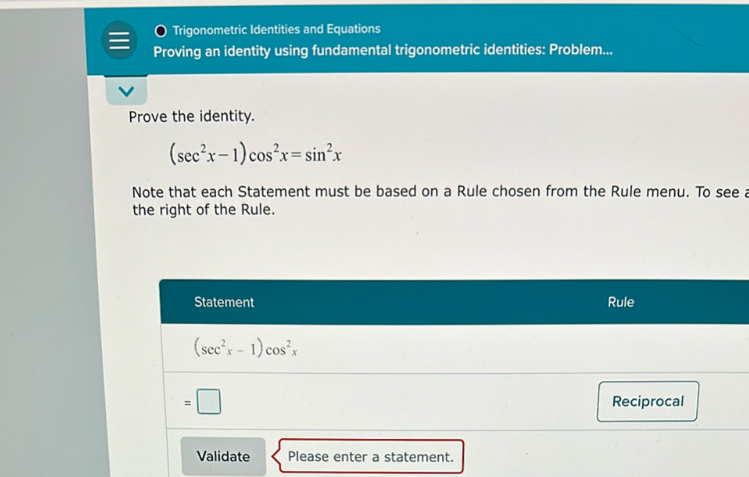
Q. Prove the identity.
- Apply trigonometric identity: We start with the left-hand side of the equation and apply the trigonometric identity .
- Simplify expression: Simplify the expression by canceling out the and .
- Rewrite using identity: Use the trigonometric identity to rewrite as .\tan^\(2(x)\cos^(x) = \left(\frac{\sin^(x)}{\cos^(x)}\right)\cos^(x)
- Cancel out terms: Simplify the expression by canceling out the terms.
- Prove identity: We have now shown that the left-hand side of the equation simplifies to , which is the right-hand side of the original equation. Therefore, the identity is proven.
More problems from One-step inequalities: word problems
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help