AI tutor
Full solution
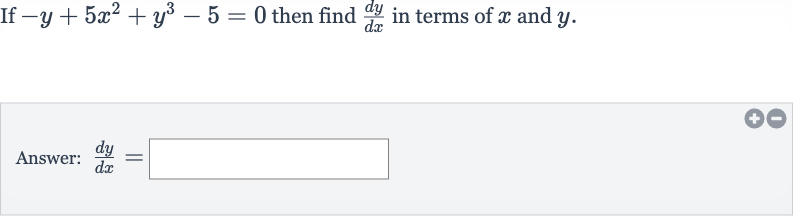
Q. If then find in terms of and .Answer:
- Differentiate : We are given the equation . To find , we need to differentiate both sides of the equation with respect to , treating as a function of (implicit differentiation).
- Differentiate : Differentiate with respect to . Since is a function of , we use the chain rule and get .
- Differentiate : Differentiate with respect to . The derivative of with respect to is .
- Differentiate : Differentiate with respect to . Again, using the chain rule, the derivative is .
- Combine differentiated terms: Differentiate with respect to . The derivative of a constant is .
- Solve for : Combine all the differentiated terms to rewrite the equation: .
- Factor out : Now, we need to solve for . Group all the terms containing on one side and the rest on the other side: .
- Isolate : Factor out from the left side: .
- Simplify : Divide both sides by to isolate : .
- Simplify : Divide both sides by to isolate : .Simplify the expression for : .