AI tutor
Welcome to Bytelearn!
Let’s check out your problem:
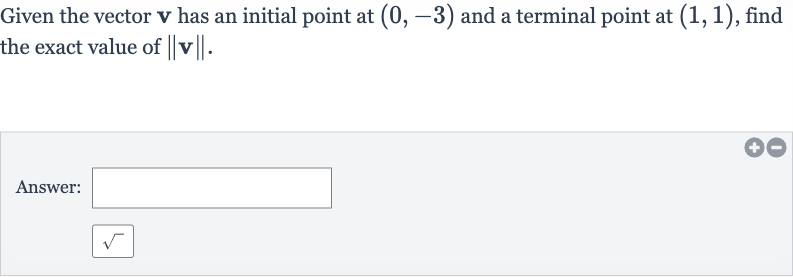
Given the vector has an initial point at and a terminal point at , find the exact value of .Answer:
Full solution
Q. Given the vector has an initial point at and a terminal point at , find the exact value of .Answer:
- Define Initial and Terminal Points: To find the magnitude of vector , we need to calculate the difference in the -coordinates and the difference in the -coordinates between the terminal point and the initial point. Then, we will use the Pythagorean theorem to find the magnitude.Let's denote the initial point as and the terminal point as .
- Calculate Differences: Calculate the difference in the x-coordinates () and the difference in the y-coordinates ().
- Use Pythagorean Theorem: Now, we use the Pythagorean theorem to find the magnitude of vector , which is denoted as .
More problems from Transformations of absolute value functions: translations and reflections
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
