Full solution
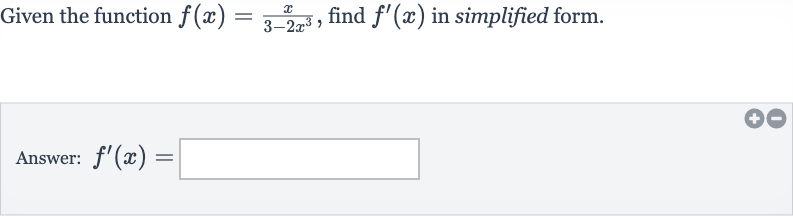
Q. Given the function , find in simplified form.Answer:
- Identify Function: Identify the function to differentiate.We are given the function . We need to find its derivative, which is denoted by .
- Apply Quotient Rule: Apply the quotient rule for differentiation. The quotient rule states that if we have a function , then its derivative is . Here, and .
- Differentiate Functions: Differentiate and .The derivative of with respect to is .The derivative of with respect to is .
- Apply Derivatives: Apply the derivatives to the quotient rule.Using the quotient rule from Step , we get:
- Simplify Expression: Simplify the expression.Now we simplify the numerator: