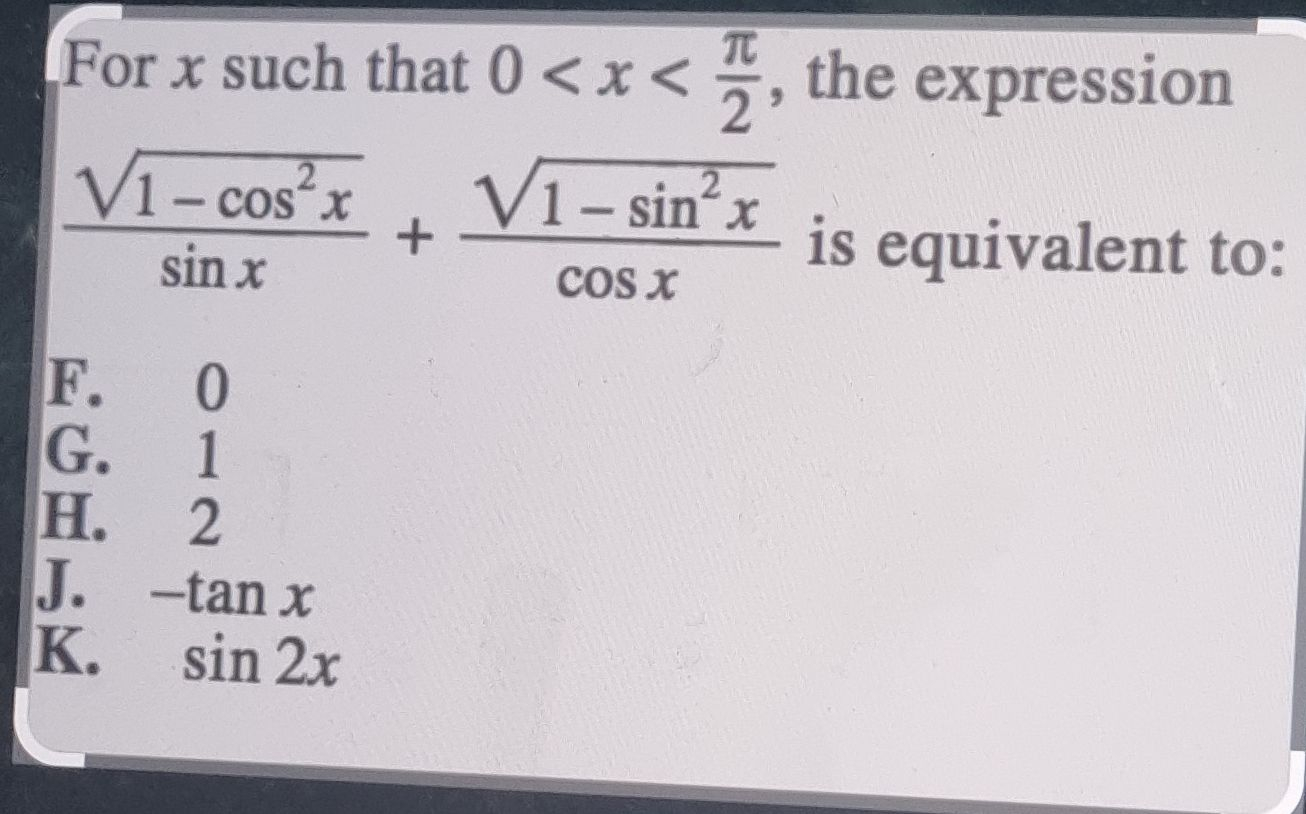AI tutor
Full solution
Q. For such that , the expression is equivalent to:F. G. H. J. K.
- Recognize Trigonometric Identities: Recognize that the expressions under the square roots are trigonometric identities. The identity can be rearranged to and .
- Substitute Identities: Substitute the identities into the original expression to simplify it. This gives us .
- Simplify Square Roots: Since we are given that 0 < x < \frac{\pi}{2}, both and are positive in this range. Therefore, we can simplify to and to .
- Combine Terms: After simplification, the expression becomes , which simplifies to .
- Final Result: Adding the two terms together, we get .
More problems from Function transformation rules
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help