AI tutor
Welcome to Bytelearn!
Let’s check out your problem:
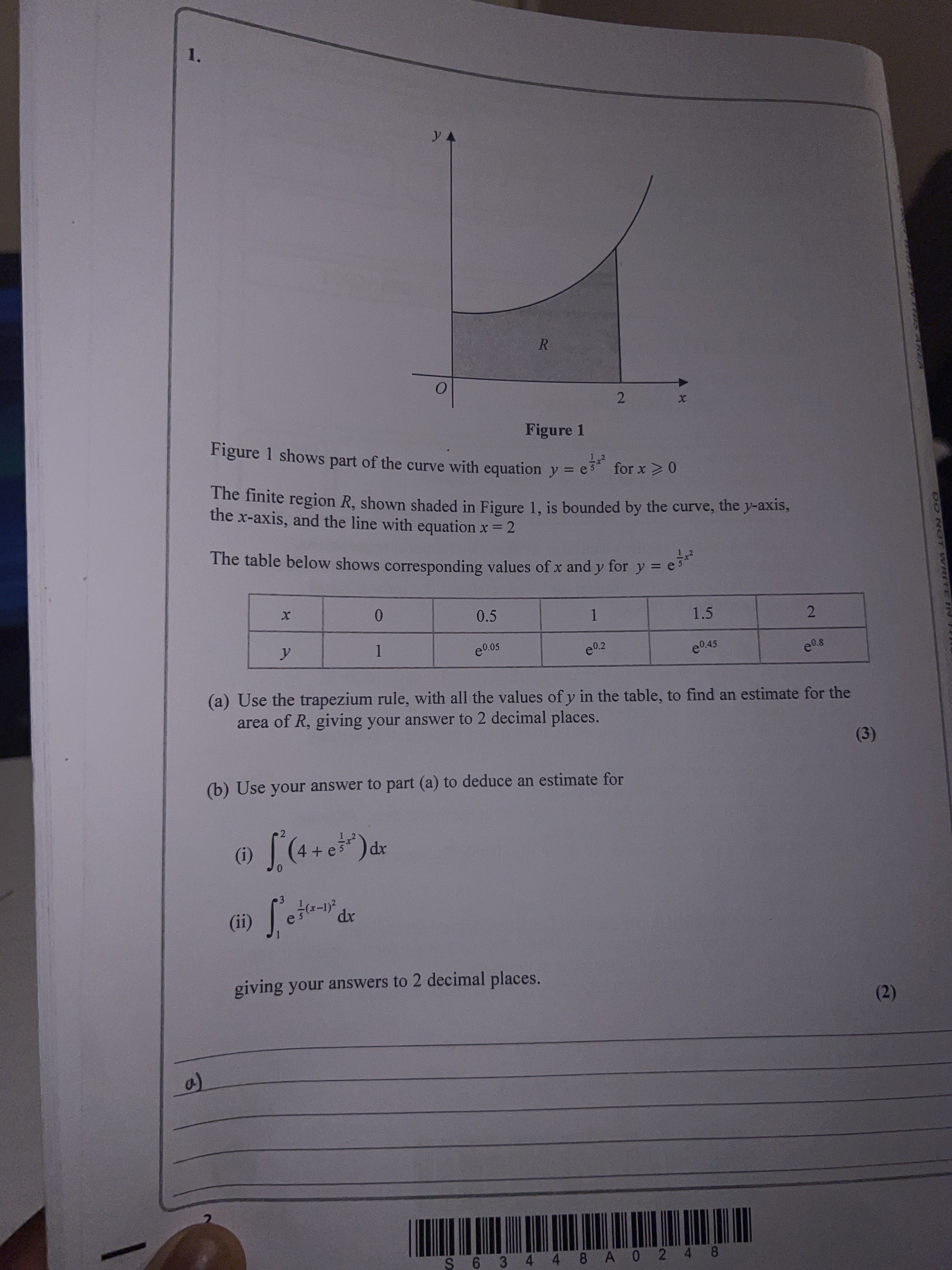
Figure Figure shows part of the curve with equation for The finite region , shown shaded in Figure , is bounded by the curve, the -axis, the -axis, and the line with equation The table below shows corresponding values of and for ..(a) Use the trapezium rule, with all the values of in the table, to find an estimate for the area of , giving your answer to decimal places. () (b) Use your answer to part (a) to deduce an estimate for (i) (ii) giving your answers to decimal places. a)
Full solution
Q. Figure Figure shows part of the curve with equation for The finite region , shown shaded in Figure , is bounded by the curve, the -axis, the -axis, and the line with equation The table below shows corresponding values of and for ..(a) Use the trapezium rule, with all the values of in the table, to find an estimate for the area of , giving your answer to decimal places. () (b) Use your answer to part (a) to deduce an estimate for (i) (ii) giving your answers to decimal places. a)
- Identify values: Identify the values of from the table.Values: , , , , .
- Calculate width: Calculate the width of each interval, ..
- Apply trapezium rule: Apply the trapezium rule formula:
- Substitute values: Substitute the values into the formula:
- Simplify expression: Simplify the expression:
- Calculate values: Calculate the values of , , , and :
- Substitute values back: Substitute these values back into the formula:
- Simplify expression inside: Simplify the expression inside the parentheses:
- Multiply by .: Multiply by .:
- Answer for part (a): Answer for part (a):
- Deduce estimate for integral: Use the result from part (a) to deduce the estimate for :
- Deduce estimate for integral: Use the result from part (a) to deduce the estimate for :Since the integral is over a different interval and function, we cannot directly use the result from part (a). This part requires a different approach.
More problems from Compare linear and exponential growth
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
