AI tutor
Full solution
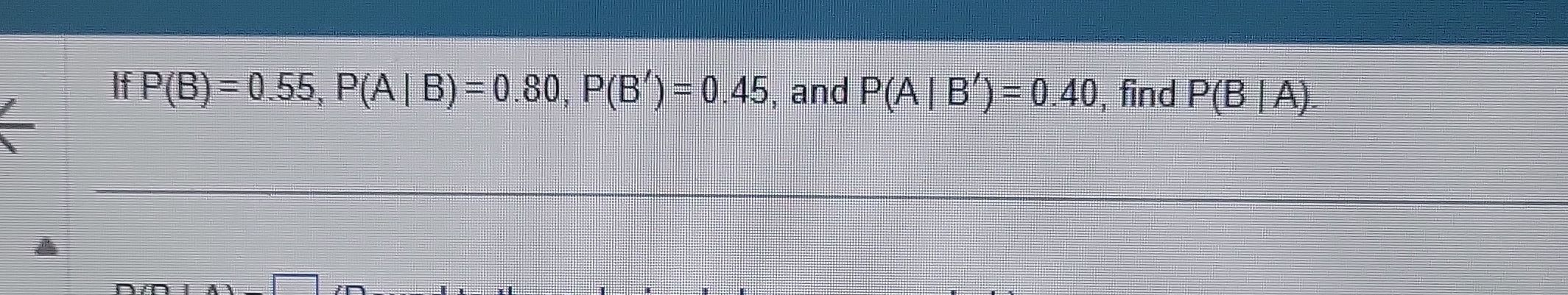
Q. If , and , find
- Rephrase Problem: First, let's rephrase the "Find the conditional probability ."
- Apply Bayes' Theorem: To find , we will use Bayes' theorem, which states that .
- Calculate : We already have and . We need to find , which is the total probability of occurring.
- Use Law of Total Probability: To find , we use the law of total probability: .
- Calculate : We have , , , and . Let's calculate .
- Calculate : Now we can calculate using Bayes' theorem.
- Simplify Fraction: Finally, we simplify the fraction to get the value of .
More problems from Evaluate expression when a complex numbers and a variable term is given
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help