AI tutor
Welcome to Bytelearn!
Let’s check out your problem:
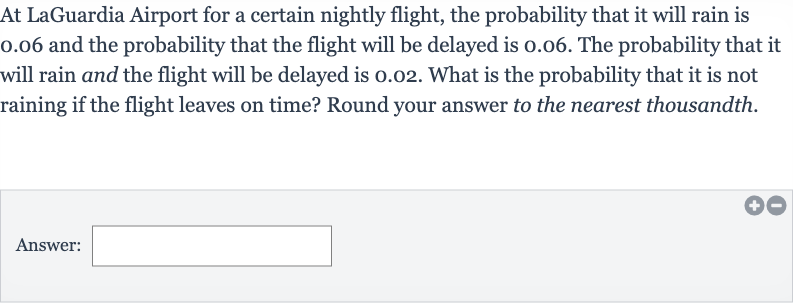
At LaGuardia Airport for a certain nightly flight, the probability that it will rain is . and the probability that the flight will be delayed is . . The probability that it will rain and the flight will be delayed is . . What is the probability that it is not raining if the flight leaves on time? Round your answer to the nearest thousandth.Answer:
Full solution
Q. At LaGuardia Airport for a certain nightly flight, the probability that it will rain is . and the probability that the flight will be delayed is . . The probability that it will rain and the flight will be delayed is . . What is the probability that it is not raining if the flight leaves on time? Round your answer to the nearest thousandth.Answer:
- Events Denoted: Let's denote the events as follows:R: It will rain.D: The flight will be delayed.We are given the following probabilities:We want to find the probability that it is not raining given that the flight leaves on time. This is a conditional probability problem, and we can use the formula for conditional probability:where is the event that it does not rain, and is the event that the flight leaves on time (is not delayed).First, we need to find , which is the probability that it does not rain and the flight leaves on time. This is the complement of the probability that it rains or the flight is delayed.To find , we use the Addition Rule of Probability:Substituting the given values, we get:Now we can find :Next, we need to find , which is the probability that the flight leaves on time. This is the complement of the probability that the flight is delayed.Now we can calculate the conditional probability:Rounding to the nearest thousandth, we get:
More problems from Find probabilities using the addition rule
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
