AI tutor
Welcome to Bytelearn!
Let’s check out your problem:
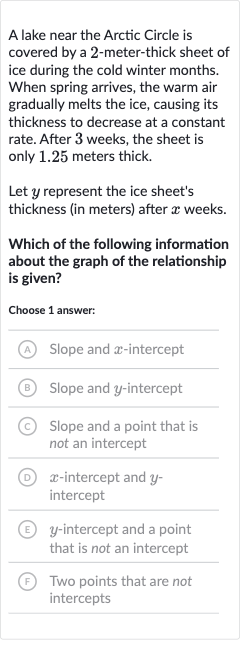
A lake near the Arctic Circle is covered by a -meter-thick sheet of ice during the cold winter months. When spring arrives, the warm air gradually melts the ice, causing its thickness to decrease at a constant rate. After weeks, the sheet is only . meters thick.Let represent the ice sheet's thickness (in meters) after weeks.Which of the following information about the graph of the relationship is given?Choose answer:(A) Slope and -intercept(B) Slope and -intercept(C) Slope and a point that is not an intercept(D) -intercept and intercept(E) -intercept and a point that is not an intercept(F) Two points that are not intercepts
Full solution
Q. A lake near the Arctic Circle is covered by a -meter-thick sheet of ice during the cold winter months. When spring arrives, the warm air gradually melts the ice, causing its thickness to decrease at a constant rate. After weeks, the sheet is only . meters thick.Let represent the ice sheet's thickness (in meters) after weeks.Which of the following information about the graph of the relationship is given?Choose answer:(A) Slope and -intercept(B) Slope and -intercept(C) Slope and a point that is not an intercept(D) -intercept and intercept(E) -intercept and a point that is not an intercept(F) Two points that are not intercepts
- Identify Initial Condition: To find the relationship between the thickness of the ice sheet and the number of weeks, we start by identifying the initial condition. At the beginning (week ), the ice sheet is meters thick. This gives us a point on the graph: .
- Determine Change in Thickness: Next, we determine the change in thickness after weeks. The ice sheet's thickness decreases from meters to meters. This change over time gives us another point on the graph: .
- Calculate Slope: To find the slope of the line that represents the relationship between the thickness of the ice sheet (y) and the number of weeks (x), we use the formula for slope: . Substituting the given points (, ) and (, .), we get . This means the thickness decreases by . meters per week.
- Find Y-Intercept: The -intercept of the graph is the thickness of the ice sheet at week , which is meters. This is given directly in the problem statement and represents the starting thickness of the ice sheet before it begins to melt.
- Conclude Relationship: Given the slope and the y-intercept, we can conclude that the information provided allows us to determine both the slope of the graph and its y-intercept. Therefore, the correct choice is Slope and y-intercept.
More problems from Slopes of parallel and perpendicular lines
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
