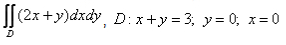AI tutor
Full solution
Q.
- Determine region D: Determine the region D for integration.The region D is bounded by the lines , , and . This forms a right triangle in the first quadrant with vertices at , , and .
- Set up double integral: Set up the double integral. Since ranges from to (from the line to the line where ), and ranges from to (from to ), the integral is set up as: .
- Integrate with respect to x: Integrate with respect to x. = = .
- Simplify expression: Simplify the expression.
More problems from Find limits involving trigonometric functions
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help