AI tutor
Welcome to Bytelearn!
Let’s check out your problem:
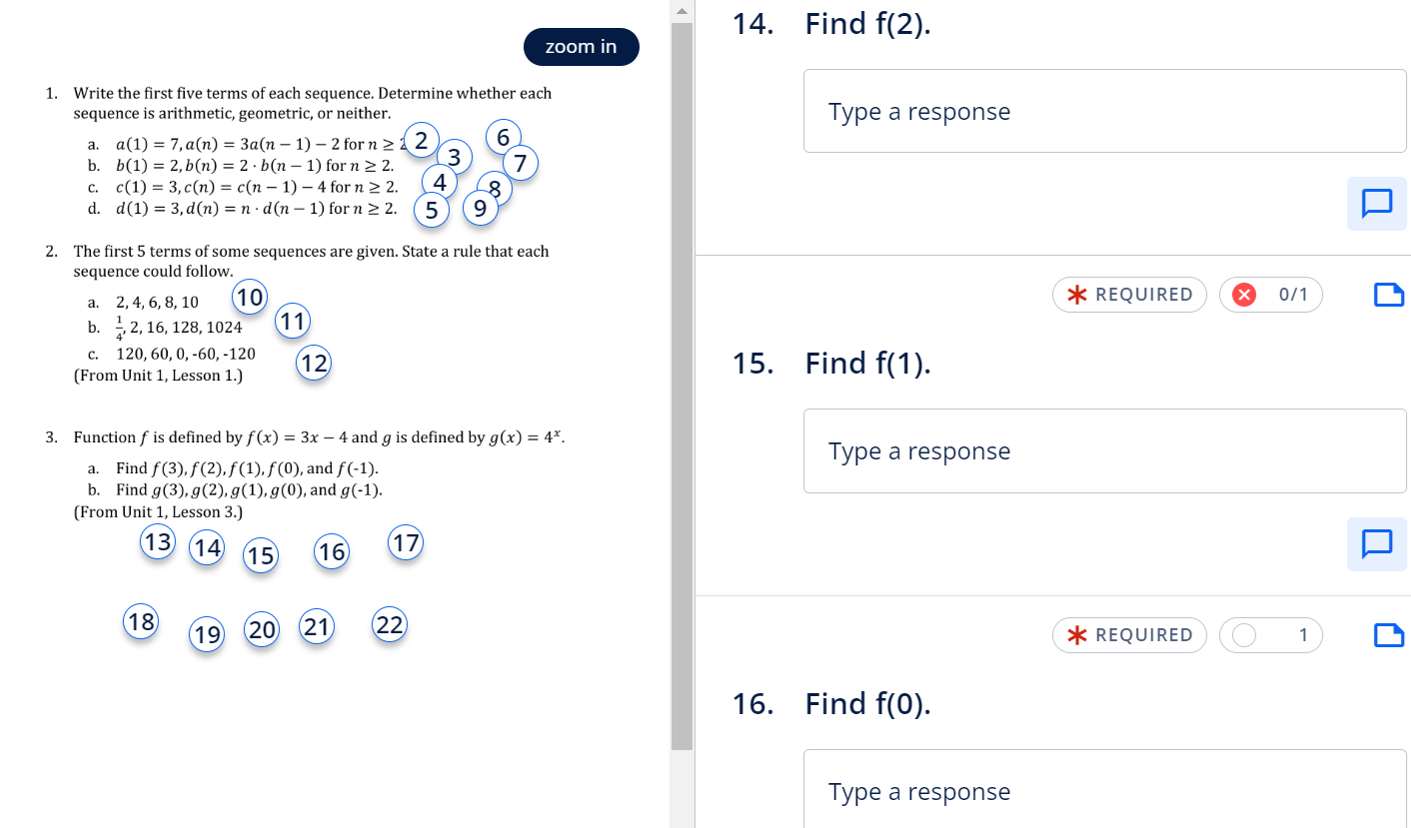
zoom in Find .Write the first five terms of each sequence. Determine whether each sequence is arithmetic, geometric, or neither.a. \quad a()=,\ a(n)=a(n) for n \geq b. \quad b()=,\ b(n)=\cdot b(n) for n \geq .c. \quad c()=,\ c(n)=c(n) for n \geq .d. \quad d()=,\ d(n)=n\cdot d(n) for n \geq .Type a responseREQUIRED Find .a. \quad ,,,,b. \quad \frac{}{},,,,c. \quad ,,,,(From Unit , Lesson .)Type a response. Function is defined by and is defined by .a. Find and .b. Find and .(From Unit , Lesson .)()() ()() () REQUIRED Find .Type a response
Full solution
Q. zoom in Find .Write the first five terms of each sequence. Determine whether each sequence is arithmetic, geometric, or neither.a. \quad a()=,\ a(n)=a(n) for n \geq b. \quad b()=,\ b(n)=\cdot b(n) for n \geq .c. \quad c()=,\ c(n)=c(n) for n \geq .d. \quad d()=,\ d(n)=n\cdot d(n) for n \geq .Type a responseREQUIRED Find .a. \quad ,,,,b. \quad \frac{}{},,,,c. \quad ,,,,(From Unit , Lesson .)Type a response. Function is defined by and is defined by .a. Find and .b. Find and .(From Unit , Lesson .)()() ()() () REQUIRED Find .Type a response
- Calculate first five terms: For sequence a, given and for .Calculate the first five terms.
- Determine sequence type: Determine if sequence a is arithmetic, geometric, or neither.Check the differences: , , , The differences are not constant, so it's not arithmetic.Check the ratios: , , , The ratios are not constant, so it's not geometric.Conclusion: Neither.
- Calculate first five terms: For sequence b, given and for .Calculate the first five terms.
- Determine sequence type: Determine if sequence b is arithmetic, geometric, or neither.Check the differences: , , , The differences are not constant, so it's not arithmetic.Check the ratios: , , , The ratios are constant, so it's geometric.Conclusion: Geometric.
- Calculate first five terms: For sequence c, given and for .Calculate the first five terms.
- Determine sequence type: Determine if sequence c is arithmetic, geometric, or neither.Check the differences: , , , The differences are constant, so it's arithmetic.Conclusion: Arithmetic.
- Calculate first five terms: For sequence d, given and for .Calculate the first five terms.
- Determine sequence type: Determine if sequence d is arithmetic, geometric, or neither.Check the differences: , , , The differences are not constant, so it's not arithmetic.Check the ratios: , , , The ratios are not constant, so it's not geometric.Conclusion: Neither.
