AI tutor
Full solution
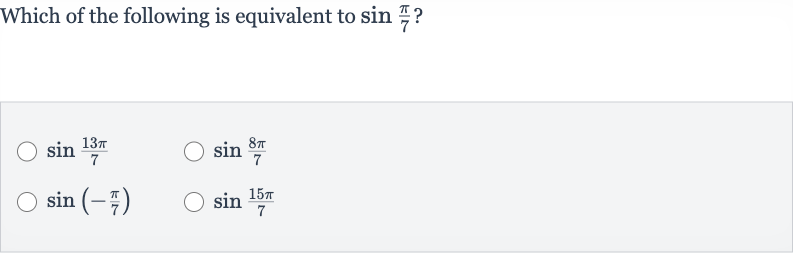
Q. Which of the following is equivalent to ?
- Properties of Sine Function: Understand the properties of the sine function. The sine function has a period of , which means for any integer . Also, for any angle .
- Evaluate : Evaluate .Since , we can use the property with to find an equivalent expression..This is not equivalent to because is not generally equal to .
- Evaluate : Evaluate .Since , we can use the property ..This is not equivalent to because is not the same angle as .
- Evaluate : Evaluate . Using the odd function property of sine, which is , we get: . This is not equivalent to because of the negative sign.
- Evaluate : Evaluate .Since , we can use the property with to find an equivalent expression..This is equivalent to because we have subtracted a full period of the sine function.
More problems from Multiplication with rational exponents
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help