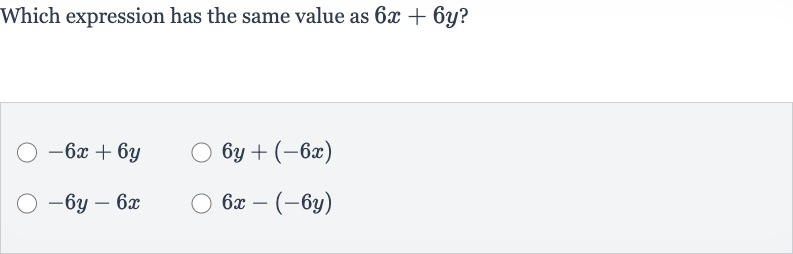AI tutor
Full solution
Q. Which expression has the same value as ?
- Identify Given Expression: Identify the given expression and the options to compare.Given expression: Options to compare: A) B) C) D)
- Compare Option A: Compare option A with the given expression.Given expression: Option A: The term in option A is the additive inverse of in the given expression, so option A does not have the same value as the given expression.
- Compare Option B: Compare option B with the given expression.Given expression: Option B: The term in option B is the additive inverse of in the given expression, so option B does not have the same value as the given expression.
- Compare Option C: Compare option C with the given expression.Given expression: Option C: Both terms in option C are the additive inverses of the corresponding terms in the given expression, so option C does not have the same value as the given expression.
- Compare Option D: Compare option D with the given expression.Given expression: Option D: The term in option D is the same as because the double negative cancels out. Therefore, option D simplifies to , which is the same as the given expression.
More problems from Simplify variable expressions involving like terms and the distributive property
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help